Health and Safety G.I Training Session,
Federal Civil Defence, Interior Ministry,
Govt. of Pakistan..
Presentation on High Explosive Charge (TNT, RDX, Black Powder) Threats,
Brisance, Shattering Capability, Detonation Velocity, and anticipated
Potential Hazard associated with the use of HE..
HOD HSE, Indus Pharma (Pvt) Ltd.
Facebook page:
(First read this)
Mechanism of an Explosion of Shock Wave
As the name suggests, this post introduces the blast wave concept by text and presentation.About Explosives!!
An explosive material, also called an explosive, is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material.
This potential energy stored in an explosive material may be
1) - Chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or grain dust
2) - Pressurized gas, such as a gas cylinder or aerosol can.
3) - Nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239
Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand.
Materials that detonate (explode faster than the speed of sound) are said to be "high explosives" and materials that deflagrate are said to be "low explosives".
Explosives may also be categorized by their sensitivity. Sensitive materials that can be initiated by a relatively small amount of heat or pressure are primary explosives and materials that are relatively insensitive are secondary or tertiary explosives.
A wide variety of chemicals can explode; a smaller number are manufactured in quantity as explosives. The remainder are too dangerous, sensitive, toxic, expensive, unstable, or decompose too quickly for common usage.
Mechanism of an Explosion:
Shock Wave (Blast Wave, Blast Radius)
This post is about the mechanism of an explosion. We all know that it creates a shock wave also known as a blast wave. You must have listened to Forensic experts on movies and TV talking about blast radius, well the radius is the distance up to which the blast wave or shock wave travels evaporating or hurling anything in its path. More the blast material in it more the radius of shock wave and more the devastation. Now i come to more technical part:
Mechanism:
This post is about the mechanism of an explosion. We all know that it creates a shock wave also known as a blast wave. You must have listened to Forensic experts on movies and TV talking about blast radius, well the radius is the distance up to which the blast wave or shock wave travels evaporating or hurling anything in its path. More the blast material in it more the radius of shock wave and more the devastation. Now i come to more technical part:
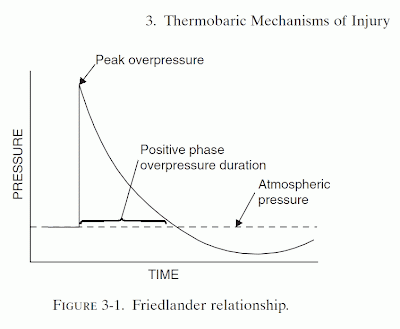 |
- Intense exothermic reaction
- Detonation: Propagation at supersonic speeds (approximately 5000 m/s) radially from the explosion.
- A shock wave (blast wave) is generated in the surrounding setting in motion the mass movement of air (the dynamic overpressure or blast wind)
- Propulsion of fragments and environmental material
- Intense thermal radiation















No comments:
Post a Comment